Video Analytics, also referred to as Video Content Analysis (VCA), is a generic term used to describe computerized processing and analysis of video streams. Computer analysis of video is currently implemented in a variety of fields and industries; however the term “Video Analytics” is typically associated with analysis of video streams captured by surveillance systems. Video Analytics applications can perform a variety of tasks ranging from real-time analysis of video for immediate detection of events of interest, to analysis of pre-recorded video for the purpose of extracting events and data from the recorded video.

Video Analytics
Video analytics is used for automated surveillance. Smart cameras with analytics continuously analyze video and can detect the presence of people and vehicles and interpret their activities. Suspicious activities such as loitering or moving into an unauthorized area are automatically flagged and forwarded to security personnel.
Various research studies and real-life incidents indicate that an average human operator of a surveillance system, tasked with observing video screens, cannot remain alert and attentive for more than 20 minutes. Similar to human vision, which has a perceptual and cognitive aspect, video analytics uses computer vision algorithms which enable it to perceive or see, and machine intelligence to interpret, learn and draw inferences. The goal of video analytics is scene understanding, which differs from motion detection. In addition to detecting motion, analytics qualifies the motion as an object, understands the context around the object, and is able to track the object through the scene.
Video Analytics is an ideal solution that meets the needs of surveillance system operators, security officers, and corporate managers, as they seek to make practical and effective use of their surveillance systems.

Video Analytics enhances video surveillance systems by performing the tasks of real-time event detection, post-event analysis and extraction of statistical data while saving manpower costs and increasing the effectiveness of the surveillance system operation.
Through the implementation of various image processing algorithms, Video Analytics can detect a variety of events, in real-time, such as:
- Penetration of unauthorized people / vehicles into restricted areas
- Tailgating of people / vehicles through secure checkpoints
- Traffic obstacles
- Unattended objects
- Vehicles stopped in no-parking zones, highways or roads
- Removal of assets
- Crowding or grouping
- Loitering and more.
- Video cameras
- Network infrastructure
- Security management solutions (Video Management Systems, Command & Control Systems etc.)
- Storage
- Video Analytics
Video Analytics can be implemented in two different configurations, which correlate to the evolution of the Video Analytics and surveillance technologies, such as :
- Server Based Implementation
- Edge Based Implementation
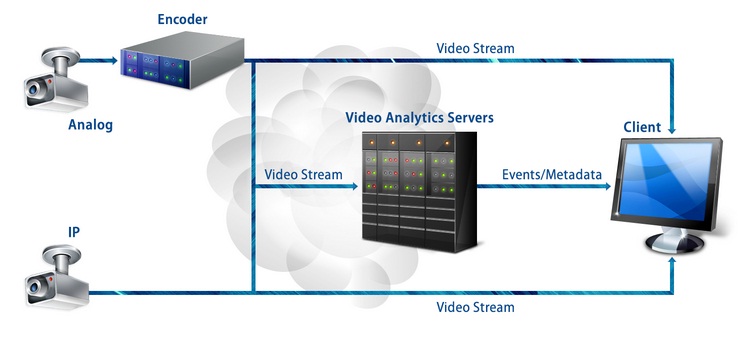
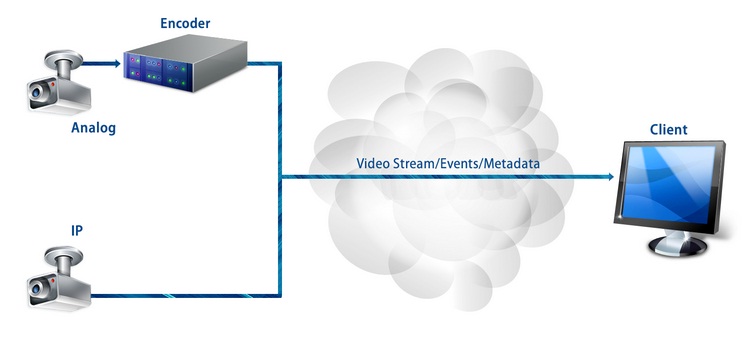
Video surveillance systems are typically installed to record video footage of areas of interest within a facility, around its perimeter or in outdoor areas which require observation, with a view to “catching” (allowing the user to be able to observe) and recording events related to security, safety, loss prevention, operational efficiency and even business intelligence.
Video Analytics can be implemented in various sectors such as :
- Banking
- Government Organizations
- Educational Institutions
- Transport(Railways/Airport)
- Hospitals / Malls /Retails
- Enterprise / Industries.,etc
Video Analytics enhances video surveillance systems by performing the tasks of real-time event detection, post-event analysis and extraction of statistical data while saving manpower costs and increasing the effectiveness of the surveillance system operation.
Through the implementation of various image processing algorithms, Video Analytics can detect a variety of events, in real-time, such as:
Left Object: When an object is left in the scene for more than predefined time, an alarm will be sent. The event will be recorded as left object in system log for later retrieval. This feature ensures security that no unidentified items are left in a defined area. The detection time is set in seconds and gives raise alarm for up to minutes. The minimum and maximum size of the object can be set.

Tailgating: This Feature detects a person (individual) or vehicle following too closely the person or vehicle in front to get past access controlled entrances or barriers. The time gap between the two successive objects is set. Any person or vehicle following within the time gap would initiate an alarm.


The application counts the people traversing a certain passage.
The installation can be done in 2 ways.
1) Angular for applications like city surveillance to cover wider area.
2) Overhead for the installation like in entry/exit points.
Accuracy 90-98%

Face Capture: Detects face in the camera FOV, captures it and stores it
Face Recognition: Matches the Face detected with the faces in the database and sends alarms.
Alarms: Option to send Alarms (Face Matching/non Matching) to VMS or Alarm Centre

Tripwire :Detection of a person or vehicle crossing (or touching) a virtual line drawn in the camera field of view. The line crossing event can be detected for both directions.
Example: Intruder detection on fenced areas, alert monitoring at the entrance, detection of illegal crossing of railway lines or getting closer to a restricted zone.

Trespass :Detection of a person or vehicle entering or exiting virtual area drawn by the user.
Example: Intruder detection in restricted areas. Illegal entry into secured zones in Banks, Stores, Plants. Entry of person or vehicle into restricted area or exit from that.
Stitches video feeds from 2-8 cameras (with 10% overlap in adjacent cameras) into a single continuous panoramic view and sends the stitched video to VMS. It also tracks object on the stitched video.
Example: Used for enhanced monitoring of large indoor and wider outdoor areas like in Airports, Railways, Border Security, large compounds, Traffic Intersections etc.

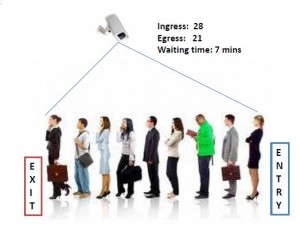
This feature provides queue properties like:
Ingress – count of people coming into queue
Egress – count of people coming out of queue
Waiting time – Waiting time in the queue.
Example: Used in service counters, ticket counters / travel desk, check in counters, flight boarding areas for waiting time analysis and improvement of service process.